Understanding Shock Collars for Dogs
Definition of Shock Collars
Shock collars, also known as electronic collars or e-collars, are devices designed to deliver an electrical stimulus to a dog’s neck through a remote control. They are often used for training purposes to curb unwanted behaviors. While the intent behind their use may be to promote obedience or deter barking, many pet owners question their safety and effectiveness.
How Shock Collars Work
Shock collars operate on a simple premise: when the owner activates the device, a brief electric shock is administered to the dog. The intensity of the shock can often be adjusted, leading to an array of potential sensations for the dog, from mild to severe. Here’s how they typically function:
- Remote Control: Owners can activate the collar to deliver a shock at their discretion.
- Sensory Feedback: Some collars provide sound or vibration before delivering a shock, intending to reinforce training commands.
While some trainers argue that shock collars can effectively suppress unwanted behaviors, it’s essential to consider the possible distress this method may inflict on dogs.
Types of Shock Collars Available
Shock collars come in various types, catering to different training needs:
- Standard Shock Collars: Basic models with adjustable shock levels.
- Barking Collars: Automatically deliver a shock when barking is detected.
- Remote Training Collars: Controlled by the owner to correct behavior on demand.
- Vibration and Sound Collars: Offer alternative stimulation without electric shocks.
While the technology may vary, the fundamental question remains: Are these collars truly effective and safe for dogs?
Risks Associated with Shock Collars
Potential Dangers of Using Shock Collars
While shock collars are marketed as a solution for training, many pet owners are unaware of the potential dangers associated with their use. Misuse or misunderstanding of the collars can lead to serious consequences, such as:
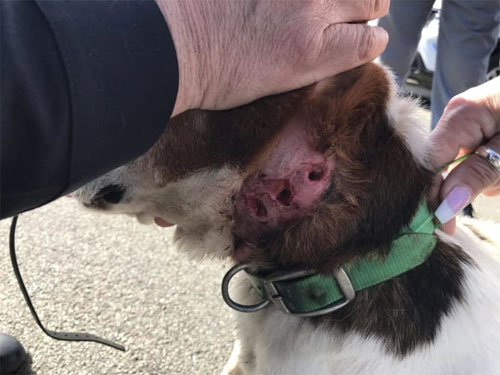
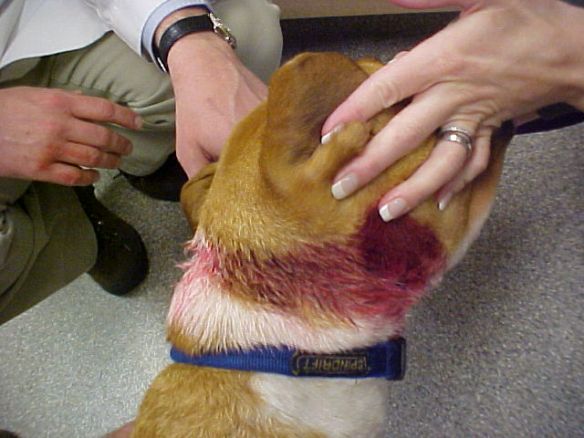
- Physical Injuries: Electric shock collars can cause burns and skin irritation, especially if used at inappropriate levels for a dog’s size.
- Behavioral Problems: Rather than correcting a behavior, shock collars can instill fear or anxiety in dogs, leading to more problematic behaviors.
Impact on the Dog’s Behavior
The psychological effects of shock collars are concerning. Many dogs may develop:
- Fear-Based Behaviors: After being shocked, a dog may start to associate the collar or specific actions with pain, which can lead to avoidance behaviors or aggression.
- Phobias: Prolonged use can result in high stress levels and phobias, impacting their overall well-being. A friend’s dog, for example, became fearful of going outside after a few negative experiences with a shock collar.
Health Risks and Side Effects
Besides psychological impacts, the physical risks cannot be ignored:
- Skin Issues: Improper use can lead to punctures and bruises on the skin due to the collar’s heaviness or poor fit.
- Burns: If the intensity is too high, it may result in severe burns, which can take time to heal, causing both physical and emotional pain.
Overall, the risks associated with shock collars extend far beyond the immediate shock, making humane alternatives a more desirable option for training.

Factors Influencing Fatality Risks
Dog’s Age and Health Condition
The age and health of a dog play critical roles in how they respond to shock collars. Puppies and senior dogs tend to be more sensitive to physical stimuli. For instance, a young puppy may not fully understand the connection between their behavior and the shock, leading to extreme anxiety. An older dog with existing health issues may experience heightened stress, which can exacerbate their condition.
- Younger Dogs: More impressionable; exposure to aversive training can instill lasting fears.
- Older Dogs: May suffer from arthritis or heart conditions, making them particularly vulnerable to stress-induced health risks.
Intensity and Frequency of Shock
The intensity and frequency of the electric shock administered can significantly affect a dog’s emotional and physical well-being. High levels of pressure are not suitable for every dog, especially if the collar is kept at a high setting for prolonged periods. Just like people, dogs have individual thresholds for discomfort and pain.
- Frequency: Continuous or frequent shocks can lead to chronic stress, causing aggressive behaviors and long-lasting psychological distress.
- Intensity Levels: The wrong settings can lead to burns or injuries, which may require medical attention.
Improper Use and Training Methods
Improper use of shock collars, including lack of training knowledge, can lead to severe consequences. Many owners may mistakenly apply a shock collar without understanding how to use it effectively.
- Training: A poorly timed shock can lead not only to confusion but also to fear of the owner. For example, if your dog barks once and receives an immediate shock without understanding its context, it can create anxiety linked to that action.
- Inconsistency: Mixed signals during training can further confuse the dog, deteriorating the human-animal bond.
Considering these factors can help pet owners make informed and thoughtful choices about their dog’s training methods while fostering a healthier, trusting relationship.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Studies on the Effects of Shock Collars
Numerous studies highlight the negative consequences of using shock collars on dogs, emphasizing not just physical harm but psychological distress. Research published in peer-reviewed journals indicates that:
- Increased Anxiety: Dogs trained with shock collars exhibited higher levels of stress and anxiety than those trained using positive reinforcement techniques.
- Behavioral Changes: Many dogs developed phobias and aggressive behaviors as a direct result of the shocks, undermining their training and socialization efforts.
This evidence starkly contradicts the claims made by proponents of shock collars regarding their effectiveness.
Real-Life Incidents and Fatalities
Real-life accounts from dog owners depict alarming outcomes linked to shock collar usage. Some unfortunate cases involve dogs that, after being shocked, developed such severe anxiety that they no longer interacted positively with humans or other dogs.
- In extreme situations, a dog’s resultant fear has led to behavior such as biting, which tragically culminated in euthanasia due to the dangers posed to both the dog and people around them.
Many owners recount a journey from loving companionship to distress and aggression, posing a critical question about the effectiveness and humanity of shock collars.
Expert Opinions on Risks Involved
Veterinary and animal behavior experts overwhelmingly agree that shock collars pose significant risks. Leading professionals stress that:
- Effective Training Alternatives Exist: Experts advocate for positive reinforcement methods, emphasizing that teaching through praise and rewards builds a bond of trust rather than fear.
- Risk of Loss of Trust: Dr. Carlo Siracusa warns that the unpredictability of shock collars can harm the human-animal bond, leading to long-lasting detrimental effects on a dog’s behavior and emotional state.
In light of these findings, it becomes imperative for dog owners to reconsider their training methods in favor of approaches that foster a healthier pet-owner relationship.

Alternatives to Shock Collars
Positive Reinforcement Training
Positive reinforcement training is a highly effective and humane alternative to shock collars. This method focuses on rewarding desired behaviors rather than punishing undesirable ones. By using treats, praise, or toys as rewards, pet owners can encourage specific actions in their dogs.
- Example: When teaching a dog to sit, providing a treat immediately after they sit reinforces that behavior. Over time, the dog connects the action with the reward, leading to consistent obedience.
Many trainers recommend building a strong reward system tailored to each dog’s preferences to maximize efficacy.
Behavior Modification Techniques
Behavior modification techniques can help address specific issues without the use of aversive tools like shock collars. Techniques such as desensitization and counter-conditioning aim to change a dog’s emotional response to triggers.
- Desensitization: Gradually exposing a dog to a feared situation in a controlled way helps reduce their anxiety over time.
- Counter-Conditioning: This involves changing a dog’s reaction to a stimulus by associating it with positive experiences, like treats or play.
These methods promote a healthier mindset and can eliminate unwanted behaviors without inflicting fear.
Safe and Humane Training Tools
In addition to positive reinforcement, many safe and humane training tools can effectively assist dog training. These include:
- Clickers: A simple device that marks desired behavior with a sound, allowing the dog to connect their action with a reward.
- No-Pull Harnesses: These harnesses help manage a dog’s pulling behavior without causing harm or discomfort.
By utilizing these positive strategies and tools, dog owners can foster a trusting, loving relationship with their pets while effectively addressing behavioral challenges. Making the switch from shock collars to humane training methods can lead to a well-adjusted and happier canine companion.

Ensuring Your Dog’s Safety
Responsible Training Practices
To ensure your dog’s safety during training, it’s essential to adopt responsible practices. This means avoiding tools that could cause harm, such as shock collars, and focusing instead on methods that build trust and understanding.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog with treats, praise, or play when they exhibit desired behaviors. This approach not only enhances learning but also strengthens your bond.
- Limit the Use of Disciplinary Measures: If your dog misbehaves, opt for redirection or time-outs instead of punishment. This can help avoid negative associations with training.
In my experience fostering rescue dogs, utilizing positive reinforcement turned a fearful and anxious pup into a confident and happy member of the family.
Signs of Distress in Dogs
Being attuned to your dog’s emotional state is vital. Signs of distress can include:
- Excessive Barking: This may indicate anxiety or fear.
- Cowering or Hiding: Dogs may hide or freeze if exposed to something distressing.
- Aggressive Behavior: Growling or snarling is a clear sign that a dog feels threatened or scared.
Recognizing these signs early can help prevent situations that may escalate into behavioral issues or physical harm.
Consulting with Veterinarians and Professionals
Consulting with veterinarians or professional trainers can provide valuable insights and help identify effective training strategies.
- Veterinarian Evaluation: Before embarking on a training journey, it’s wise to have your dog evaluated for any health issues that could affect their behavior.
- Professional Trainers: Seek out trainers who emphasize positive reinforcement techniques. Their expertise can guide you in addressing specific behavioral problems without resorting to harmful methods.
By adopting these practices, you can create a safe and fulfilling training environment that enhances your dog’s well-being and strengthens your relationship. Remember, a happy dog leads to a happy home!
Conclusion
Summary of Risks Associated with Shock Collars
As explored throughout this discussion, shock collars carry significant risks that can jeopardize a dog’s well-being. The electric shocks can lead to physical injuries, psychological distress, and altered behaviors. Many dogs subjected to these devices become anxious, fearful, or even aggressive, straying far from their original temperaments. Moreover, the probability of developing serious health conditions, such as cardiac arrhythmias, raises further concerns regarding their use.
- Pain and Discomfort: Even at mild settings, the shock can be unpleasant and lead to minor injuries.
- Behavioral Impact: Dogs may develop phobias or aggression, making them less social and more difficult to manage.
- Impact on Human-Animal Bond: The emotional toll of using shock collars can deteriorate the bond between the dog and owner, leading to trust issues.
Considerations for Choosing Safe Training Methods
When considering training methods for dogs, prioritizing humane and effective approaches is paramount. Here are a few considerations:
- Positive Reinforcement: Leverage treats, praise, and affection to encourage desirable behaviors.
- Consult Professionals: Seek guidance from qualified trainers who utilize science-backed, compassionate training techniques.
- Monitor Your Dog’s Behavior: Be attentive to your dog’s reactions and be prepared to adjust your methods if signs of distress arise.
Choosing safe training methods not only enhances obedience but also nurtures a loving relationship, ultimately leading to a happier and healthier canine companion. Remember, a trusting bond is fundamental to a positive pet experience, and patience is key to your training success.

Leave a Reply